 What is dental erosion or tooth decay?
What is dental erosion or tooth decay?
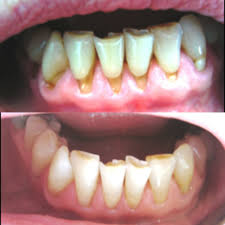
Dental erosion is a permanent loss of dental tissue, caused exclusively by the action of acids on the surface of the toothpaste. Dental erosion is a major problem in modern society, due to a specific, modern way of life, which involves consuming large amounts of acidic food (sour fruits), and large amounts of acidic and carbonated drinks, especially beverage types.
The origin of the acid can be different: the external acids are introduced into the body by food or drink, while the internal acid is caused by the return of gastric acid (hydrochloric acid) in gastrointestinal disease or frequent vomiting.
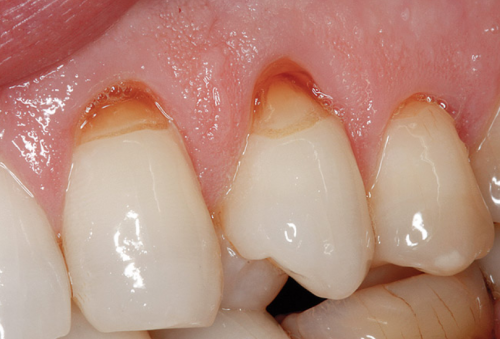
What changes occur on teeth in erosion – teeth wear?
Changes in the teeth are almost imperceptible until the thickness of the tooth is reduced. Over time there is a complete disappearance of the envelope, so erosion is impenetrable, and it involves dentin. Only then is the first symptom of increased sensitivity (hypersensitivity) of dentine, which is manifested as short-term pain when taking chilled or acidic food and drink, and also when washing teeth.
What are the causes of dental erosion?
Dental erosion occurs as a result of chronic exposure to the external and internal acids.
External acids in the oral cavity come from the outer environment – through nutrition (most often in the form of acidic foods and drinks) or as air pollution in certain environments. Sources of acids can be foods: fruit (lemon, apple, orange, etc.), tomatoes, mustard, ketchup, drinks (especially carbonated: coca-cola, sprite, boys, mineral water), fruit juices (orange, grapefruit, etc.), energy drinks and sports drinks, and alcoholic beverages (especially white wine). These include some medicines (inhalation drugs used in asthma therapy and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease – HOBP), as well as preparations such as: effervescent C-vitamin, C-vitamin in chewable tablets, and iron-containing beverages.
Internal acid – gastric acid – it gets into the oral cavity due to frequent vomiting (once a week or more often) caused by psychological disorders or due to the return of gastric contents due to digestive tract disorders, gastroesophageal reflux. Since gastric acid has a much higher acidity than the critical acidity of the saliva, which causes salivation, this means that long-lasting hydrochloric acid reflux in the oral cavity can cause large losses in dental structures.
Factors that affect the occurrence of dental erosion
Factors that affect the occurrence of dentane erosion are: chemical factors, biological factors and behavior (bad habits) of people.
Chemical factors – the most common cause of dental erosion is the acid-containing dishes and beverages. Increased consumption of fruit drinks (which is a citric acid) is generally considered to be very healthy, however, the negative influence of acid on the health of teeth is often neglected. However, foods like different types of yogurt and other dairy products, despite their higher acidity, do not act erosively because they are rich in calcium and phosphates.
Biological factors that affect the occurrence of dental erosion include: the flow and composition of the saliva, the composition and structure of the teeth, as well as the position of soft tissues and tongue in relation to teeth.
Bad habits affecting the onset of dental erosion
The onset of dental erosion is influenced by the following habits:
– inadequate way of ingesting acidic food (by sipping or holding mouth sutures);
– prolonged exposure to acid, high incidence and excessive intake of erosive agents, and inadequate oral hygiene;
Brushing teeth with a hard toothbrush (with strong pressure);
– use of a tooth whitening paste;
– tooth whitening with strong acids in the dental office;
– Drug addiction (cocaine and ecstasy). The onset of dental erosion in these individuals is associated with the consumption of large amounts of acidic beverages – due to dehydration and decreased salivation of the saliva.
Occupations where dental erosion occurs more often
Dental erosion is often classified as a category of professional illness:
– in people who daily test wine (oenologist and somelian), due to tasting by shaking wine in the oral cavity – in order to feel better his taste, the dental surfaces are constantly covered with this drink. The increased risk of dental erosion occurs due to the high acidity of the drink, as well as due to the reduced levels of calcium and phosphate ions in the saliva.
– in people working in factories exposed to the evaporation of industrial acids, as well as in biochemical laboratories, daily contact with inorganic and organic acids at work can increase the frequency of dental erosion;
– For athletes – professional swimmers, divers and water polo players – dental erosion is caused by the use of chlorine in pools, as well as low pH of water, given the fact that they spend more than 30 hours a week in such water.